Scientists have mapped an insect brain in greater detail than ever before |
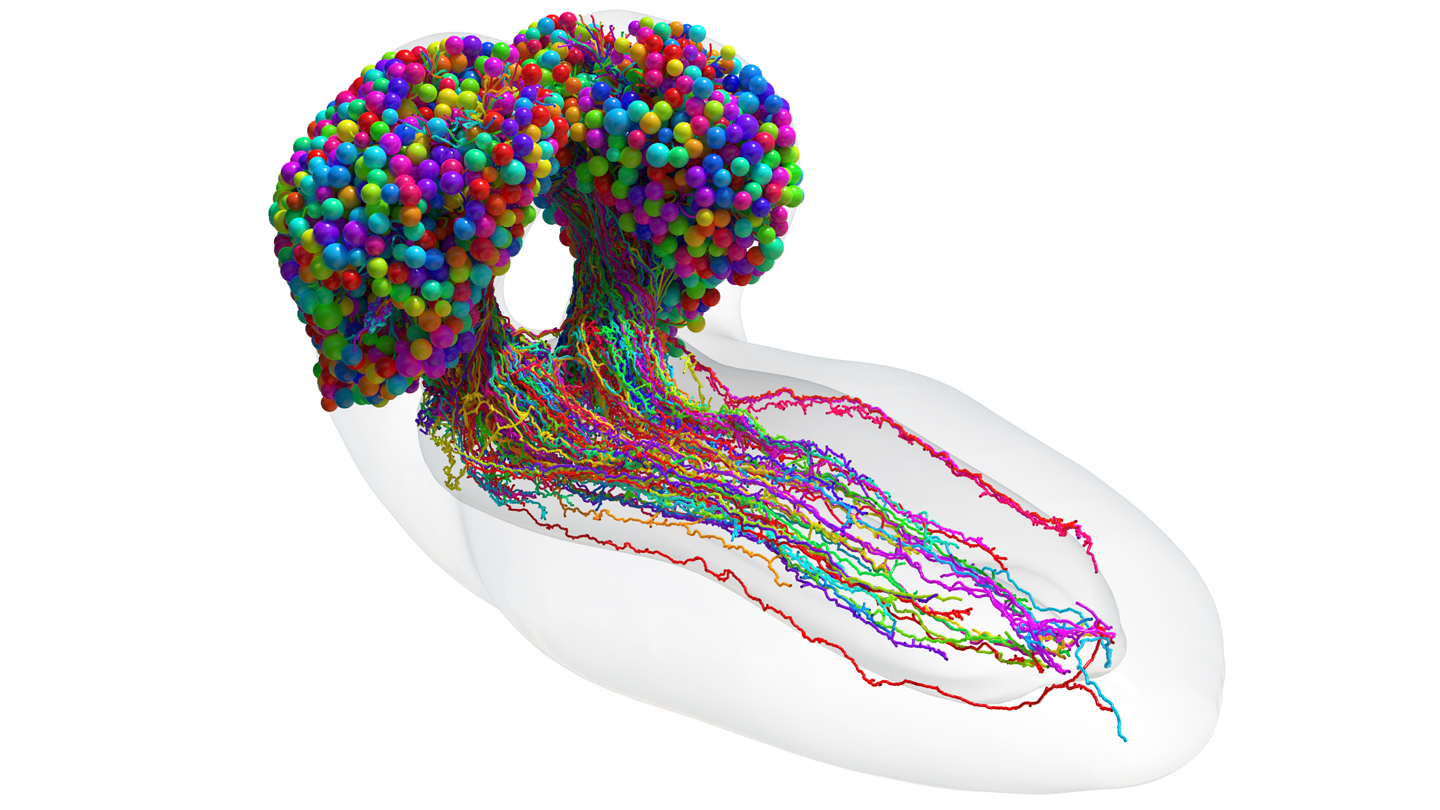 |
| Every print subscription comes with full digital accessThis diagram shows every nerve cell (multicolor) in a larval fruit fly brain, with the spheres representing the cell body and the elongated tails as branches that send and receive information. The connections, known as synapses, aren’t visible here.Michael WindingBy McKenzie PrillamanThe wiring of one insect’s brain no longer contains much uncharted territory.All of the nerve cells — and virtually every connection between them — in a larval fruit fly brain have now been mapped, researchers report in the March 10 . It’s the most complex whole brain wiring diagram yet created. Previously, just three organisms — a sea squirt and two types of worm — had their brain circuitry fully diagrammed to this resolution. But the brains of those creatures have only a few hundred neurons. The scientists who conducted the new study wanted to understand much more complicated brains.Headlines and summaries of the latest Science News articles, delivered to your email inbox every Thursday.Thank you for signing up!There was a problem signing you up.Fruit flies () share a wide range of behaviors with humans, including integrating sensory information and learning. Larvae perform nearly all the same actions as adult flies — except for some, like flying and mating — but have smaller brains, making data collection much faster ().The idea for this project came 12 years ago, says neuroscientist Marta Zlatic of the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, England. At that time, she and her colleagues captured electron microscope images of the entire larval fruit fly brain. They then stitched those images together in a computer and manually traced each neuron to create a 3-D rendering of the cells. Finally, the team found the connections where information gets passed between the cells, and even determined the sending and receiving ends.The researchers identified more than 3,000 neurons and about 550,000 connections, known as synapses.Neurons transmit information to one another in circuits. Exploring the neurons’ connectivity patterns — not just directly linked partners, but also the links of linked cells and so on — revealed 93 different types of neurons. The classes were consistent with preexisting groupings characterized by shape and function. And nearly 75 percent of the most well-connected neurons were tied to the brain’s learning center, indicating the importance of learning in animals.The researchers hope that this work serves as a blueprint for fellow scientists studying brain circuitry. “Now we have a reference map,” Zlatic says.Questions or comments on this article? E-mail us at feedback@sciencenews.org | Reprints FAQM. Winding . The connectome of an insect brain. . Vol. 379, March 10, 2023, p. 995. doi: 10.1126/science.add9330.McKenzie Prillaman is the Spring 2023 science writing intern at . She holds a bachelor’s degree in neuroscience with a minor in bioethics from the University of Virginia and a master’s degree in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz.Our mission is to provide accurate, engaging news of science to the public. That mission has never been more important than it is today. As a nonprofit news organization, we cannot do it without you. Your support enables us to keep our content free and accessible to the next generation of scientists and engineers. Invest in quality science journalism by donating today.Science News was founded in 1921 as an independent, nonprofit source of accurate information on the latest news of science, medicine and technology. Today, our mission remains the same: to empower people to evaluate the news and the world around them. It is published by the Society for Science, a nonprofit 501(c)(3) membership organization dedicated to public engagement in scientific research and education (EIN 53-0196483). © Society for Science & the Public 2000–2023. All rights reserved. Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the archives and digital editions.Not a subscriber? Become one now. |
Mar 10th, 2023 |
| source |